Module 1:
Object orineted Programing ; Managed Language & C#
What is Object Oriented Programming
To be object oriented, a language is designed around the concept of objects. that are something, have certain properties and exhibit certain behaviors. This means the language generally includes support for: —
Encapsulation — Inheritance — Polymorphism
What is Managed Language
Managed languages depend on services provided by a runtime environment.
• C# is one of many languages that compile into managed code.
• Managed code is executed by the Common Language Runtime (CLR).
• The CLR provides features such as: — Automatic memory management — Exception Handling — Standard Types — Security
There are 3 categories of types:
— Value types : these directly store values
— Reference types:or objects, store a reference to data
— Pointer types:only available in unsafe code
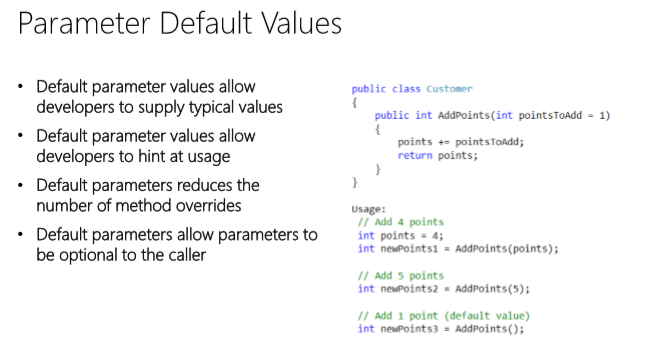
What are Lambda Expressions
- An enhancement of anonymous methods
- • An unnamed method written inline
- • An alternative to a delegate
- • At compile time a lambda expression becomes either: — An instance of a delegate — Or an expression tree
- • Expressions are validated at compile time, but evaluated at run time.
- • Dynamic expression trees are supported
Module 2:
Constructing Complex Types, Object Interfaces and Inheritance and Generics
Classes and Structs
• A class or struct defines the template for an object.
- A class represents a reference type
- A struct represents a value type
- Reference and value imply memory strategies
When to Use Structs :
Use structs if:
— instances of the type are small
— the struct is commonly embedded in another type
— the struct logically represent a single value
— the values don’t change (immutable)
— It is rarely “boxed” (see later)
• Note: structs can have performance benefits in computational intensive applications
Note : Useful : 2 classes inside same namespace
Inheritance
— Classes can optionally be declared as:
- static — can never be instantiated
- abstract — can never be instantiated; it is an incomplete class
- sealed — all classes can be inherited unless marked as sealed
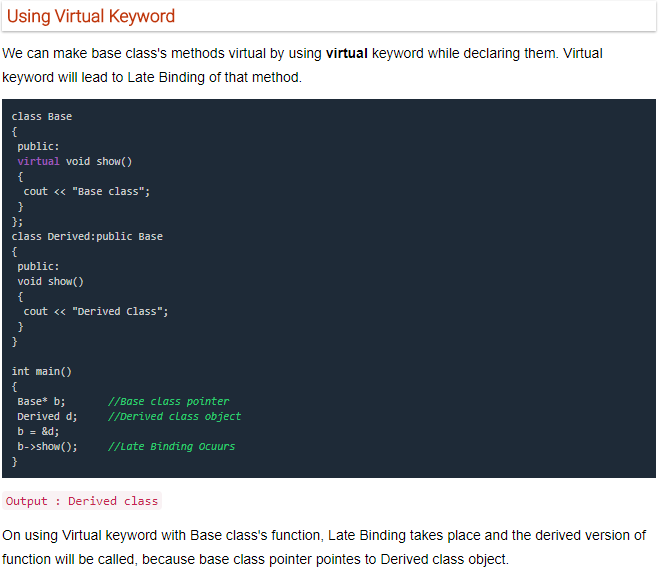
— Virtual Methods
- Virtual methods have implementations
- They can be overridden in derived class.
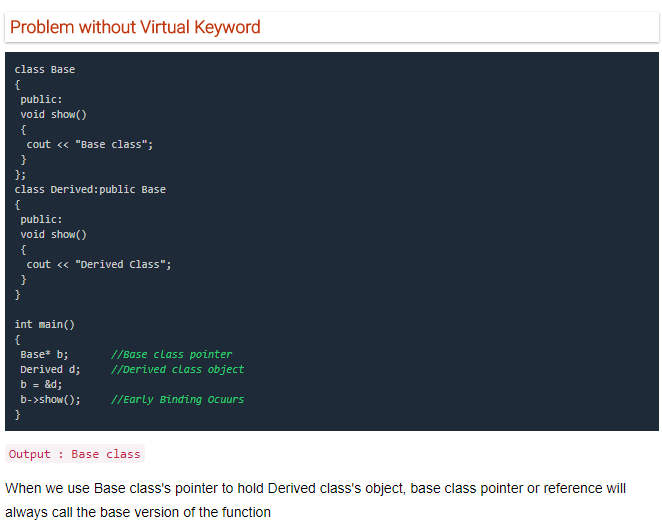
What are Virtual Functions
Virtual Function is a function in base class, which is overrided in the derived class, and which tells the compiler to perform Late Binding on this function.
Virtual Keyword is used to make a member function of the base class Virtual.
Example :
Module 3:
Controlling Programmatic Flow & Manipulating Types and Strings
Module 4:
Code Reflection and Information ,Working with Garbage Collection
What is Reflection
Reflection inspects type metadata at runtime
The type metadata contains information such as:
- The type Name
- The containing Assembly
- Constructors
- Properties
- Methds
- Attributes
- This data can be used to create instances, access values and execute methods dynamically at runtime
What is Garbage Collection
Garbage collection is automatic memory management.
• De-referenced objects (orphans) are not collected immediately but periodically.
- factors influence Garbage Collection frequency —
- Not all orphans are collected at the same time
Garbage Collection is computationally expensive
Memory Leaks
- Despite having automatic memory management, it is still possible to create managed memory leaks.
- • Objects that fall out of scope may be referenced by objects in scope, keeping them alive.
- • Events can be a common source of memory leaks:Events can hold references to objects ,Solution! Unsubscribe from events proactively
- • Weak references can be used to avoid some memory leak scenarios
Weak Reference
- Weak references create a reference that the Garbage Collector ignores.
- • The Garbage Collector will assume an object is eligible for collection if it is only referred to by weak references.
- • To hold an object with only weak references, create a local variable referring to the weak reference value.
— This prevents collection until the local variable is out of scope.
Module 5:
Type and Value Validation , Encryption Technique
What is Data Validation
- Data validation is testing values introduced to an app (via a service, file, or data entry) against expected values and ranges.
- Prevent overflow
- Prevent incorrect results
- Prevent undesirable side-effects
- Provide guidance to systems or users
- Prevent security intrusions
The compiler validates that the object type is correct — It does not validate the object’s value
- Debug / Trace Assert() methods alert the developer or the user
- Raise an Exception:
— System.ArgumentException
— System.ArgumentOutofRangeException
— System.ArgumentNullException
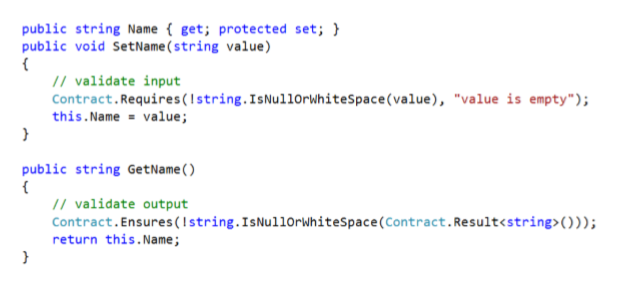
Data Contracts
- “Design by Contract” from the Eiffel programming language
- Code contracts are a unified system that can replace all other approaches to data validation
- Code contracts have — Preconditions (Requires) — Post-conditions (Ensures)
- A contract assertion can be “evaluated” statically
- A contract assertion can be “enforced” at runtime
What is Encryption
- An encryption algorithm makes data unreadable to any person or system until the associated decryption algorithm is applied.
— Encryption does not hide data; it makes it unreadable
— Encryption is not the same as compression
- Types of encryption
— File Encryption
— Windows Data Protection
— Hashing, used for signing and validating
— Symmetric and Asymmetric
Simple Encryption Mehtods
- File Encryption
— Encrypts and decrypts files
— Fast to encrypt/decrypt
— Based on user credentials
- Windows Data Protection
— Encrypts and decrypts byte[]
— Fast to encrypt/decrypt
— Based on user credentials
Hashing
One-way encryption
• Common algorithms:
— MD5 (generates a 16 character hash than can be stored in a Guid)
— SHA (SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512)
Fast (depending on chosen algorithm)
- Used for storing passwords, comparing files, data corruption/tamper checking — Use SHA256 or greater for passwords or other sensitive data
Symmetric Encryption
- One key is used for both encryption and decryption
- Faster than asymmetric encryption
• Cryptography namespace includes five symmetric algorithms:
— Aes (recommended)
— DES
— RC2
— Rijndael
— TripleDES
Asymmetric (or Public Key) Encryption
- One key is used for encryption and another key for decryption
- Commonly used for digital signatures
- Cryptography namespace includes four asymmetric algorithms:
— DSA
— ECDiffieHellman
— ECDsa
— RSA (most popular)
More Notes from NSM Subject : http://telegra.ph/Network-Security--Management-Notes-05-28-2
Code Snippet For Encryption in C# :https://gist.github.com/harshityadav95/8f332c8889d93823e79435b110078a0c
Module 6:
Splitting Assemblies and Projects , Diagnostics and Instrumentation
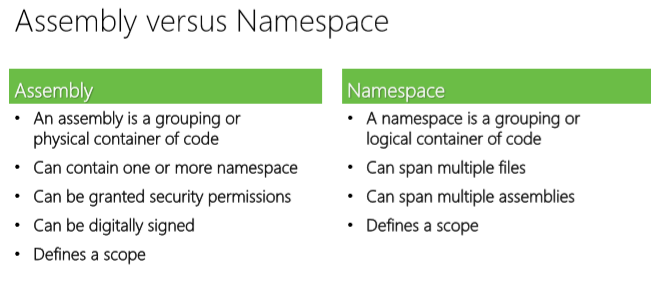
What is an assembly?
- An assembly is a container for a set of resources and types.
- Assemblies can be referenced by other assemblies.
- Some assemblies are specific to certain technologies.
- In Visual Studio, an assembly equates to a Project
What is Instrumentation?
- Instrumentation is code that reports performance information.
- Telemetry aggregates instrumentation for analysis.
- Diagnostics or Analysis is the use a telemetry to track causes of errors or identify trends.
What is a Performance Counter?
- Performance Counter is a sampling for a single operation
- You write to a counter by incrementing or decrementing
— Trending is accomplished using tooling
• You must have permission
• Counters are typically categorized
Module 7:
Interacting with File System, Working With REST Services
Why read or write to the file system?
- Show existing data to user
- Integrate user-provided data
- Serialize objects out of memory
- Persist data across sessions
- Determine environment configuration
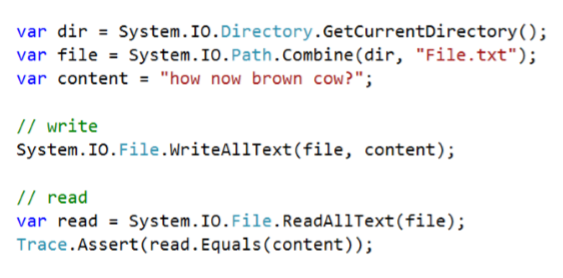
How do we write to files?
- This is simplified with Framework methods; open / shut — File.WriteAllText / ReadAllText
- Open for reading to keep open and keep writing
- Open as stream for large payloads and realtime processing
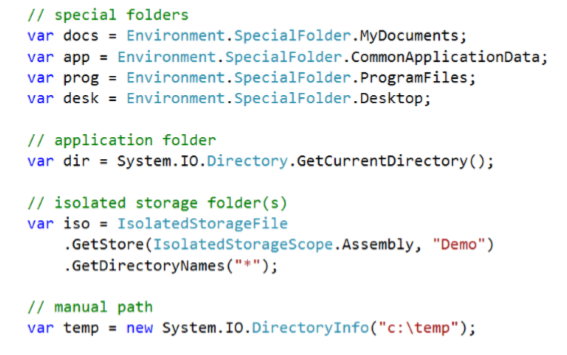
How do we find files?
- Get Windows folder with Environment Special Folders
- Get the Current folder with File.IO Get Current Directory()
- Use Isolated Storage dedicated to the current application
- Anything Else. Caveat: Windows Store App development
How do we modify files?
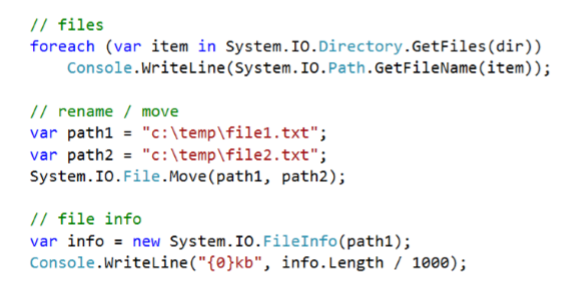
- Iterate through files using GetFiles()
- Rename / Move with System.IO methods
- Get File Info with System.UI.FileInf
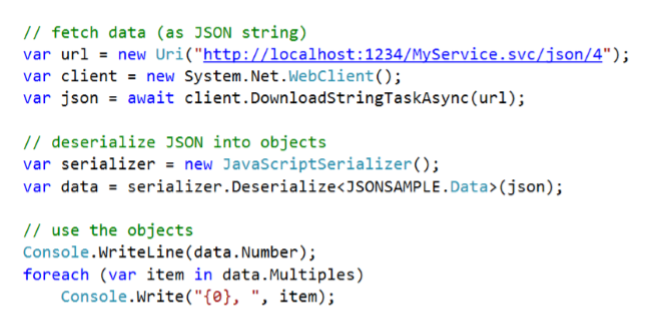
What are Web Services?
- Web Services encapsulate implementation
- Web Services expose to disparate system
- Web Services allow client systems to communicate servers — Web protocols (HTTP, GET, POST, etc)
- Web Services are important to Service Oriented Architecture
— With and without metadata
— Loose coupling
What is SOAP?
- SOAP is a standard for returning structured data from a Web Service as XML
— Envelope
— — — Header
— — —Bod
What is asynchronous programming ?
- Asynchronous maximizes resources on multicore systems, by allowing units of work to be separated and completed.
- Asynchronous programming frees up the calling system, especially a user interface, as to not wait for long operations.
What is the C# ASYNC/AWAIT keywords
- Async and await simplify asynchronous programming.
- Async and await allow asynchronous code to resemble the structure of synchronous code.
- Methods marked with async may return Task<T>.
- The async keyword instructs the compiler to allow await.
- The await keyword instructs the method to return.
- The await keyword instructs the compiler to resume execution within the same context after the operation is complete
Module 8:
Accessing a Database , Using LINQ
(More Notes on C# to JSON)
What databases can we use?
- Windows Azure SQL Database
- Local Network SQL Server
- Local Machine SQL Server Express
- Application SQL LocalDB
- Application SQL CE
- Other providers: Oracle, SqLite, MySql, DB2, Jet
— ADO.Net implements a provider model enabling many (if not all) databases. Database implementation is abstracted.
Types of access to a database
- Low-level — Manual queries — DbDataReader
- Object Relationship Models (ORM)
— Conceptual Modelling
— Entity Framework, Nhibernate, CSLA, Dapper
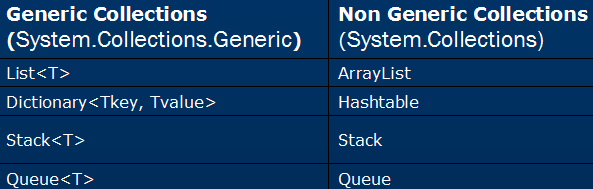
What is Language Integrated Query
- LINQ is a general-purpose Query Language
- LINQ is an integrated part of the .Net languages
- LINQ is Type Safe and has Intellisense
- LINQ includes operators like Traversal, Filter, and Projection
- LINQ can be optimized with compiler versions
- LINQ can be invoked using its Query Syntax
- LINQ can be invoked using its Method Syntax
Reference :



























No comments:
Post a Comment